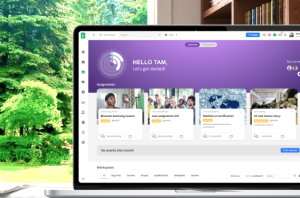
How do you decide whether the additional functionality of an LXP aligns with your business needs?
Two acronyms have emerged in corporate learning: LXP (Learning Experience Platform) and LMS (Learning Management System). Have you ever thought about the differences between LXP vs LMS?
An LMS is a crucial tool for managing learning programs and ensuring compliance, which is vital for many businesses, especially healthcare and manufacturing, where strict rules and regulations are in place.
On the other hand, an LXP is an extension of an LMS, offering extra features to democratize learning. These additional functions, such as personalization and knowledge sharing, create a collaborative and fun learning culture–supporting self-development through upskilling and reskilling initiatives.
But how do you decide whether the additional functionality of an LXP aligns with your business needs?
Start by asking, “What precise objectives do we aim to fulfill within our learning and development strategy?” Your answers will determine if investing in the enhanced capabilities of an LXP is the appropriate choice.
What is an Learning Experience Platform (LXP)?
While the LXP and LMS markets have grown dramatically over the past few years, the LXP market has seen a huge increase. According to a market research analysis, the global LXP market was USD 508.5 Million in 2020 and is now estimated to reach USD 2.18 Billion by 2026–a rate of 25.3% CAGR.
Also known as LEP (learner experience platform), an LXP is a customizable, corporate learning solution used by HR and learning and development (L&D) teams. These customizable solutions help companies provide employees with personalized and intuitive learning experiences. By using previous engagements based on their personal career progressions and interests, organizations can tailor L&D activities to suit individual needs.
Put simply, LXPs work in a similar way to how Amazon, the e-commerce giant, offers personalized customer pathways. The brand suggests products based on users’ browsing and purchase history. This approach enhances the customized shopping experience on the platform.
LXPs, like Blossom, use customization similar to Amazon’s personalization pathways. This allows employees to access relevant content via adaptive learning paths for personalized skill development. The platform has learning libraries that include access to internal training courses and third-party learning, for example, videos, podcasts, and the latest articles–driven by employees and artificial intelligence (AI).
Let’s take a look at the main features that make LXPs stand out from traditional LMSs:
- Content curation. LXPs often include robust content curation tools that allow L&D administrators, trainers, and employees to sort diverse learning materials.
- Adaptable learning. Employees can have personalized learning paths based on their preferences, skills, and learning objectives. This adaptability enhances the relevance of the learning experience, knowledge levels, and learning pace–increasing engagement.
- Social learning tools. LXPs typically include social learning features like discussion forums and chats to facilitate interaction, knowledge sharing, and employee collaboration.
- User-generated content: Many LXPs allow learners to create and share content–creating a lively and team-oriented learning space.
- Gamification elements. Gamification makes the learning experience more interactive and enjoyable. Since gamified learning content improves employee performance, badges, leaderboards, and rewards are commonly integrated into LXPs to enhance learner engagement and motivation.
- AI-powered recommendations and analytics. AI is frequently used in LXPs to analyze user behavior, preferences, and learning patterns. For example, when a learner engages with video content related to customer service, AI can recommend additional resources, enhancing the experience and encouraging further exploration of related content.
Overall, LXP features collectively contribute to unique learning experiences by focusing on adaptability, personalization, and engagement.
So, what are the differences between LXP vs LMS?
Unlike LXPs, traditional LMS software usually offers a less flexible solution for L&D. Whereas LXPs are employee-driven, LMS uses administrators who traditionally assign and track highly structured learning content.
Let’s explore five primary distinctions between LXP and LMS and their approaches to learning.
1. User-centric vs. admin-centric
A user-centric approach prioritizes the employee’s perspective throughout the L&D journey. It ensures the design, delivery, and learning content are tailored to their needs, preferences, and professional aspirations.
Rather than throwing hundreds of different courses at your employees, an LXP uses past interactions and behaviors to offer learning events that make logical sense. This user-centric approach emphasizes self-directed learning and greater autonomy to explore and engage with content.
On the flip side, LMS platforms are usually admin-centric–focusing on managing and tracking learning activities with less control over training programs and compliance requirements. The primary focus is on administrative functions and the management of training programs instead of offering meaningful, user-focused training experiences.
2. Content delivery and curation
LMS platforms typically focus on structured learning paths and course delivery. Content is often organized in a linear way, and the emphasis is on managing and tracking formal training programs.
Many traditional LMS platforms can be inflexible, making it challenging to adapt quickly to changes in learning needs or content formats.
By contrast, LXP prioritizes content curation with a personalized learning experience. It allows users to access a variety of content types, including user-generated content, videos, articles, and other resources. This means content discovery is often driven by user preferences and previous learning events, also known as content mapping.
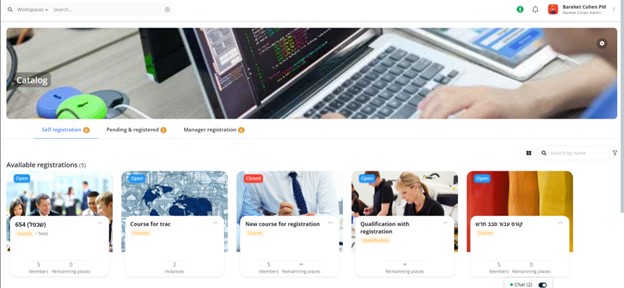
Not only that, LXP content can be curated from many sources, including third-party providers. With employees able to post educational material on the platform, LXPs are like powerful content hubs that bring together a wide variety of externally sourced and user-generated learning materials–saving time and money.
“Before Blossom, it was very complicated and time-consuming tracking and managing training for our teams, as well as onboarding new employees. This problem has been alleviated with Blossom. It has saved time for managers now with a much faster and more efficient system. It has also saved us money since we used to invest a lot in third-party tutorials, which managers can now create themselves conveniently within Blossom.” –Doron Batsir, 365 Implementer IT Department at Plasson Ltd
LXP solutions typically have content indexing for organizing and cataloging learning content. Considering the average employee spends 51% of their working day on low to no-value tasks, like finding what they need, content indexing makes searching for learning activities easier and more accessible.
3. Social learning
Sharing and transferring knowledge among employees allows you to tap into the collective wisdom of a group and learn from each other. Employees with different levels of expertise come together to share knowledge and support each other’s growth. Social learning promotes collaboration and the development of critical skills.
Since LMS solutions are usually better suited for formal learning environments with a structured curriculum, some social learning features, such as collaborative tools and discussion forums, may be limited.
By contrast, LXPs thrive in informal learning scenarios. Employees can interact through forums and online learning communities to collaborate on projects and share resources. Learning from peers often involves practical, real-world examples. This application-oriented learning helps employees understand how knowledge is used in real-life job situations, making the content more relevant and applicable. In summary, LXPs actively encourage social learning and collaboration–making it a more adaptable and lively way of upskilling and reskilling.
4. Integration and functionality
Older LMS systems may use outdated technology, leading to compatibility issues with modern devices and browsers. This can result in a poor user experience and challenges for business leaders.
Plus, some LMS platforms face difficulties scaling up to accommodate the growing needs of larger organizations or a rapidly increasing workforce. As the number of users on an LMS increases, the platform may encounter performance bottlenecks. This can result in slow loading times, lag in accessing content, or delays in tracking and reporting user progress.
By using the collective intelligence of the growing workforce, LXPs use collaborative features to create a supportive learning environment. Organizations gain a scalable knowledge-sharing system as more employees share, promoting ongoing learning and adaptability in a growing workforce.
In addition, LXPs offer integration with other systems and tools, such as HR software, applicant tracking systems, and content storage. This integration streamlines administrative tasks and reduces repetitive operations.
Blossom, for example, gives fast integration that efficiently empowers complete digitization. With its advanced digital workspaces, the Blossom LXP is designed to allow organizations to modernize for the 21st century.
5. Tracking and reporting
Some LMSs are designed primarily for compliance training, which may lead to a lack of focus on more dynamic and engaging learning experiences. Typically designed to monitor completion rates, assessment scores, and compliance records, LMS solutions focus on formal metrics.
On the other hand, LXP tracking and reporting are more focused on user engagement and content usage. Metrics may include participation in forums, content contributions, and social interactions–giving you real-time insights into informal learning behaviors. LXPs often use skills mapping to align learning content with the skills that individuals need to develop.
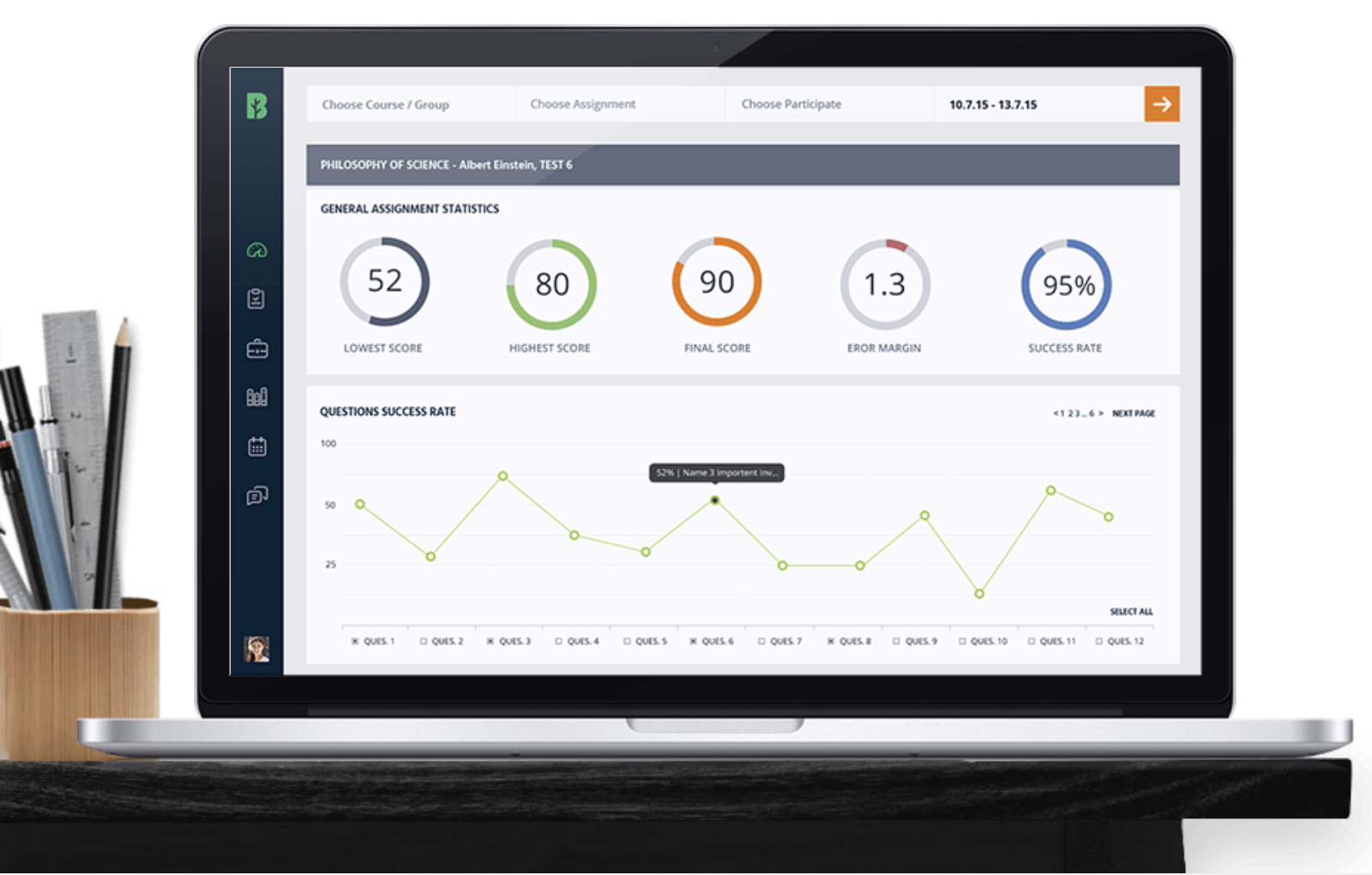
Let’s put that into perspective and say your organization needs to report on broad groupings or categories for a set of related skills. Using the context of IT, skill categories might include cybersecurity, programming languages, or even database management. Specific employee competencies or abilities might include Java programming or network security.
LXPs allow you to understand skills taxonomies–valuable for talent management, workforce development, and training program design. They help you align L&D initiatives with the skills needed to achieve strategic objectives.
Feel confident to make the right decision about your learning platform
Choose the right LXP or LMS to meet your organization’s unique needs. While LMSs are great at handling organized, formal training with features such as tracking and reporting, modern LXPs provide the same capabilities while prioritizing a more learner-focused, personalized, and informal learning approach.
Now you know the differences between LMX vs LXP. Contact us so we can curate a specific system that suits your learning needs. Schedule a demo today.